
What is an API proxy?
Understand what an API proxy is and the benefits of using it.
Posted
Updated
This article explains a fundamental principle and is up-to-date.
In general, a proxy is something that acts as an agent or intermediary for something else. An API proxy provides an interface to developers for accessing backend services and sits between the application and the backend.
What is an API proxy?
💰 The Pragmatic Programmer: journey to mastery. 💰 One of the best books in software development, sold over 200,000 times.
An API proxy acts as a handler between a consumer and backend services. It is a shim (layer of code, which provides compatibility between different interfaces), which handles data transformations, security, routing, and more. It exposes an interface customized for the consumer (web, mobile,...), makes the API calls to the different backend services on behalf of the consumer.
Let's look at some examples:
-
A modern web application needs to get information from a legacy backend services that communicates in XML. Instead of making the web application calling the legacy API, an API proxy can handle this, and the web application can communicate with the shim JSON formatted. The API proxy will translate the JSON requests into XML and call the legacy API and then return and transform the payload and send it back to the web application.
-
Another example is when a web application has to make several API calls to get data from different backend services. This could be aggregated in an API proxy and only one call made to the API proxy from the web application, and the API proxy calls the other backend services.
An API proxy is an intermediary and helps a consumer get the data from backend services, without having to talk to all the services directly. It is a layer of abstraction between the consumer and the backend.
The API proxy pattern allows to expose a stable interface to the consumers. If a backend service changes, the adaptions can be made in the API proxy layer without having to change how the frontend consumes data. An API proxy also allows an easy implementation of caching of expensive calls to backend services and can improve performance. The downside is that latency between backend and frontend will be increased minimal.
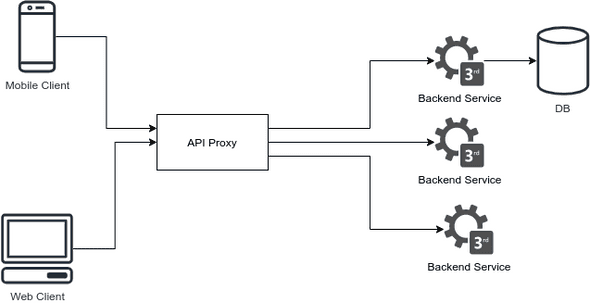 Structure of an API Proxy
Structure of an API Proxy
TL;DR
- An API proxy is an interface that sits between frontend, and the backend services.
- It decouples the frontend from implementation details of the backend.
- Complex calls to multiple backend services can be simplified for the frontend.
- Large and slow results from backend services can be cached.
Thanks for reading and if you have any questions, use the comment function or send me a message @mariokandut.
If you want to know more about Node, have a look at these Node Tutorials.
References (and Big thanks):
Newsletter Signup
Never miss an article.